The fundamental ideas of object-oriented programming, or OOPs, are class and object, which are used to represent ideas and entities found in the real world.
Class is a blueprint for the object with detailed description. Class is a base of a Object Oriented Programming. It is a container that binds data and its associated functions together in a single unit.
Object is an instance of a class . class is a logical representation whereas object is a physical representation. when we create a class for that don’t get memory . when we create a instance of class i.e. object we get the memory to perform operations on it.
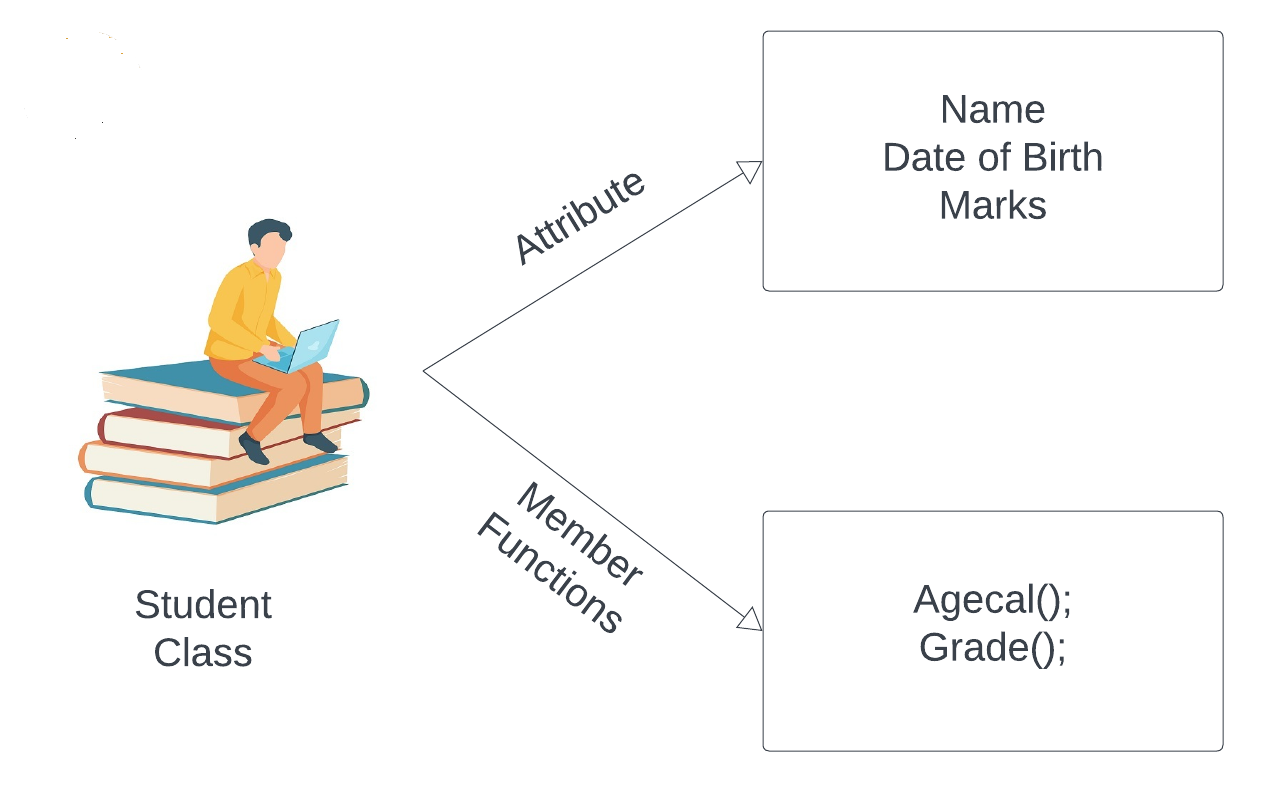
Eg. If we consider Student as a class then name, date of birth, marks of the student etc. will be the variables of the class student and
age calculation using date of birth , Grades calculation using marks will be the member functions of the class.
Class and Object in C++
Class :
- Class data is divided in
(a)Private
(b)Protected
(c)Public - Bydefault data is private
- Class allows the concept of inheritance
- We can able to make secure application
Syntax of class :
class className
{
Access specifier:
data members;
member functions();
};Object :
- Object is a instance of class
- Object is a class variable
- Object is a physical representation of class
Syntax of object :
className objectName;Difference between the class and structure
| CLASS | STRUCTURE |
|---|---|
| Classes are of reference types | Structures are of value types |
| All the reference types allocated on heap memory | All the value types are allocated on stack memory |
| Allocation of large reference type is cheaper than allocation of large value type | Allocation and de-allocation is cheaper cheaper in value types than small reference types |
| class is generally used in large programs | Structures used in small programs |
| class can be inherit from another class | structure is not allowed to inherit from another structure or class |
| The data members of a class can be protected | The data members of structure can be protected |
| Member functions of a class can be virtual or abstract | Member functions of structure cannot be virtual or abstract |
C++ Code
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class student {
int id;
char name[20];
public:
void get()
{
cout<<" Enter student Id ";
cin>>id;
cout<<" Enter student Name ";
cin>>name;
}
void put();
};
void student::put()
{
cout<<" Printing Student Information "<<endl;//std::cout
cout<<" Id : "<<id<<endl;
cout&<<" Name : "<<name<<endl;
}
int main()
{
student s;
s.get();
s.put();
return 0;
}You can download C++ for windows Click here