Babur was the founder of the Mughal Empire which was established in 1526 after Babur
defeated Ibrahim Lodi in the first battle of Panipat. Thus a new epoch and a new empire
in India began, lasting for nearly three centuries beginning from 1526 to 1857. Six major
rulers of this dynasty, Babur, Humayun, Akbar, Jahangir, Shah Jahan, and Aurangzeb,
known as the “Great Mughals”, left their mark on Indian history. The empire declined
after the death of Aurangzeb in 1707.
Babur (1526 – 1530)
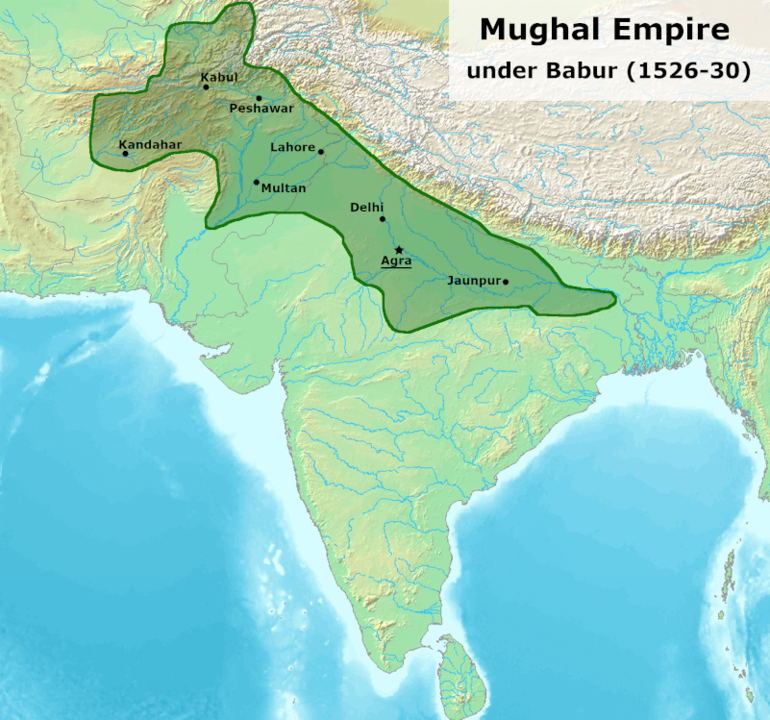
In 1526, Babur attained victory in the Battle of Panipat against Ibrahim Lodhi. The Battle
of Panipat featured the foundation of the Mughal hegemony of India. He seized Delhi and
founded the greatest regime in north India—The Mughal Empire.
The Mughal Empire was founded by Timurid prince Zahir-ud-din Muhammad Babur. He
was the heir of Timur from his father’s side and Genghis Khan from his mother’s side. He
took over Fargana at a very young age. He confronted several wars and was so savage on
the battlefield that he was labeled as a ‘tiger’.
Daulat Khan, the most significant noble of Punjab, who was dissatisfied with Ibrahim Lodhi,
invited Babur to capture India and expel Ibrahim Lodhi in the First Battle of Panipat in
1526.
The forces of Babur and Rana Sanga met at Khanwa, a place near Fatehpur Sikri. Rana
Sanga was defeated in 1527 and once again the superior military tactics of Babur
succeeded. With the defeat of Rana, the biggest challenge in north India was shattered.
(Battle of khanwa 1527). Though the Mewar Rajputs received a great shock at Khanwa,
Medini Rai at Malwa was still threatening to challenge the authority of Babur.
In the next year, Babur defeated Medini Rai in Chanderi. (Battle of Chanderi 1528). In the subsequent year, Babur encountered Afghans(Ibrahim Lodi’s brother Mohammad Lodi) and defeated them in the Battle of Ghagra in 1529. He was a scholar of Persian and Arabic languages. He wrote his autobiography, Tuzuk-i-Baburi in the Turki language. Later it was translated into Persian and other languages.
Babur was the champion of a highly developed system of warfare which was the outcome
of a scientific synthesis of the tactics of the assorted Central Asian people. Babur overly
used gunpowder in wars and on the other side, Ibrahim fought with traditional methods
ignorant of modern ways. Babur invaded Delhi and sent his son Humayun to seize Agra.
Babur called himself “Emperor of Hindustan”. On December 26, 1530, Babur died at
Agra aged 40. His body was first laid at Arambagh in Agra but was later taken to Kabul,
where it was laid to rest.
Humayun (1530-1540 and 1555-1556)
After the death of Babur in 1530, his son Humayun succeeded him. Humayun means “fortune” but he remained the most unfortunate ruler of the Mughal Empire. Humayun, a cultured and learned person, was not a soldier like his father. He was faced with the problems of a weak financial system and the predatory Afghans.
The growth of Afghan power in the regions around Bihar and Uttar Pradesh under the leadership of Sher Khan (later Sher Shah) made Humayun initiate action. Defeating the Afghans at Daurah in 1532 Humayun besieged the powerful fort of Chunar. However, in 1539 Sher Shah Suri defeated Humayun in the Battle of Chausa. Somehow Humayun managed to escape from the battleground. In the next year, SherShah Suri confronted Humayun in Kannauj and defeated him completely. (Battle of Kannauj 1540) Sher Shah started his independent rule.
Sher Shah Suri(1540-1555)
Sher Shahs Uri was the founder of the Suri dynasty after defeating the Mughal emperor Humayunh in 1540. His capital was in Sasaram in modern-day Bihar. He was the person who introduced the “rupee” in the calculated system of revenue. Sher Shah Suri was very brave and he ruled over Bihar. He changed some ruling posts and introduced many posts which have been divided into the Sarkars post.
Sher Shah Suri was one of the greatest leaders among the Muslim rulers of India. He
brought some private posts such as the administrative army and taxation posts. He built
roads, houses rents, and many well-being things for the people. He was known for
introducing the postal for the people of the Indian continent.
Akbar (1556 to 1605)
Akbar was only thirteen years old at the time of Humayun’s death. When his father died, Akbar was at Kalanaur in Punjab and therefore his coronation took place in Kalanaur itself in 1556. It was his tutor and Humayun’s favorite and confidant Bairam Khan, who served as the regent of the Mughal emperor from 1556 to 1560 . As a conqueror, Akbar triumphed all over North India. The first four years of Akbar’s rule saw the expansion of the Mughal empire from Kabul to Jaunpur, including Gwalior and Ajmer, under his regent Bairam Khan. One of the major achievements of his regency period was the defeat of Hemu and the Afghan forces in the second battle of Panipat in 1556, who were posing a serious threat to the Mughal Empire.
Jahangir (1605-1627)
Akbar was succeeded by his son Salim with the title Nur-uddin Jahangir.
He was Akbar’s son by a Rajput wife. His ascension was challenged by his
eldest son Prince Khusrau who staged a revolt with the blessings of Sikh Guru Arjun Dev.
Prince Khusrau was defeated, captured, and blinded, while Guru Arjun Dev was executed.
In 1608 Ahmad Nagar in the Deccan had declared independence under Malik Ambar.
During the reign of Jahangir, there was no addition to the Mughal territory in Deccan.
From great-great-grandfather to father, the Mughals had supported the arts, setting the
precedent for Shah Jahan. He was fascinated by painting and jewelry, as his father
Jahangir had been, and the fine arts flourished under Shah Jahan as they had in no
previous reign.
Shah Jahan (1628-1658)
According to art historian Milo Beach, “He was well known as a connoisseur of jewels. He had time to dabble in the arts and was maybe even a jewel carver himself. But clearly, his real engagement was with architecture.” Like his grandfather, Akbar the Great, Shah Jahan was passionate about architecture. Not content with the hand-me-down buildings in Akbar’s Red Fort, he replaced them with resplendent palaces of pure white marble.
As soon as the Agra Fort was completed, he moved the Mughal capital from Agra back to the ancient site of Delhi where he built a magnificent new city, owing nothing to his ancestors, yet keeping the long-established legacy of the Delhi throne. (The palaces of Shahjahanabad, now Old Delhi, are also faced entirely in white marble. Consequently, the reign of Shah Jahan is sometimes referred to as the “reign of marble.”)
Aurangzeb (1658-1707)
Aurangzeb’s full name was Muḥī al-Dīn Muḥammad. He was the third son of the Fifth emperor of the Mughal dynasty, Shah Jahan. His mother was Mumtaz Mahal. He was born on November 3, 1618, in Dhod, Malwa, India. He was the sixth emperor of the Mughal dynasty and under him, the empire rose to its greater heights. Aurangzeb was given the title of Alamgir which means conqueror of the world. Aurangzeb was considered to be the most ruthless leader who went on to create a “golden age” of Indian civilization.
Aurangzeb was the sixth ruler of the Mughal Empire who ruled over the
entire Indian subcontinent for 49 years. He was an orthodox religious Sunni Muslim ruler
and was a very good administrator. He compiled the Fatawa-e-Alamgiri and established
Sharia law and Islamic economics throughout the Indian subcontinent. He is praised
throughout history for being the most accomplished military leader but he is also
considered to be the most controversial one. Aurangzeb ruled the Mughal Empire from
1658 to 1707 and he died on March 3, 1707, in Bhingar, Ahmednagar, India.
Literacy Sources of the Mughal Empire
Baburnama/Babur Description of Hindustan
- It is written originally in Chagatai Turkic his mother tongue.
- Baburnama, an autobiography of Zahiruddhin Muhammad Babur was written in his mother tongue, Chagatai Turkic. Babur, the founder of the Mughal Empire in India, wrote this in the form of memoirs.
- It is considered the first true work in the Islamic literature of the autobiographical genre, and it contains information on Babur’s birth in 1529.
- It is also called Tuzuk-e-Babri. It ranks among the best autobiography in the world.
- It is better translated into Persian. It is transled to Persian Abdul Rahim khane-khana.
- It was translated into English by Beveridge and according to Beveridge, it is one of those priceless records of all time that is generally not available in any period.
- He appreciated the intellectual attendance of Hindustan.
Some more Sources
Humayun Nama :- Gulbadan Begum was a Mughal princess and the daughter of Emperor
Babur, the founder of the Mughal Empire. She is best known as the author of Humayun-
Nama, the account of the life of her half-brother, Emperor Humayun, which she wrote at
the request of her nephew, Emperor Akbar.
Tarik-e-shershahi :- Abbas khan sherwani wrote this book.
Akbar Nama :- Akbar Nama was wroted by Abul Fazal. There are three volumes. The third
volume is called Ain, and it is called Ain-e-Akbari.
1. The first volume deals with the first 17th years of the Akbar period.
2. The second volume deals with the rest of the periods.
3. The third volume talks about details of economy and dimension, it is called Ain-eAkbari.
Mutkhas-ul-Tawarik book- He wrote by Badauni. Badauni was highly critical of Akbar. He
gives you an analysis of Akbar.
Related to Aurangzeb : Alamgirnama by Mohamad Kazim, Muntakhab ul Lubab by Shafi
khan. Futuhat-e-Alamgiri by Ishwar dash nagar. Masir-e-Alamgiri by Saqi mutaid khan.
Sources:- Rajasthani sources and European sources.
Rajasthani sources like Ardha Kathak by Banaras Das Jain And vir Vinod of Shyamal das.
We are dependent on European sources. For example- Pasarts account, Dutch account,
and we have accounts of some French travelers like Bernier, and Tavernier.
Persian Sources:- This is the official account.
Pre & Mains : Buy History NCERT 11th class by R.S.Sharma for UPSC
History Optional : Buy A History of Ancient And Early Medieval India : From the Stone Age to the 12th Century By Upinder Singh
Inline Image Credit and License :- Wikimedia Commons license
Feature Image Credit and License :- Wikimedia Commons license
